共计 5253 个字符,预计需要花费 14 分钟才能阅读完成。
-
是人的问题? -
是事儿的问题? -
是人和事儿的关系的问题? -
人和事儿的关系的规则问题? -
Who is involved with or most affected by the problem? -
What is happening? -
When did it happen? Is it urgent? -
Where did it happen, and does it affect anything else? -
Why is the issue impacting workflows and team members? -
How is it impacting workflows and team members?
-
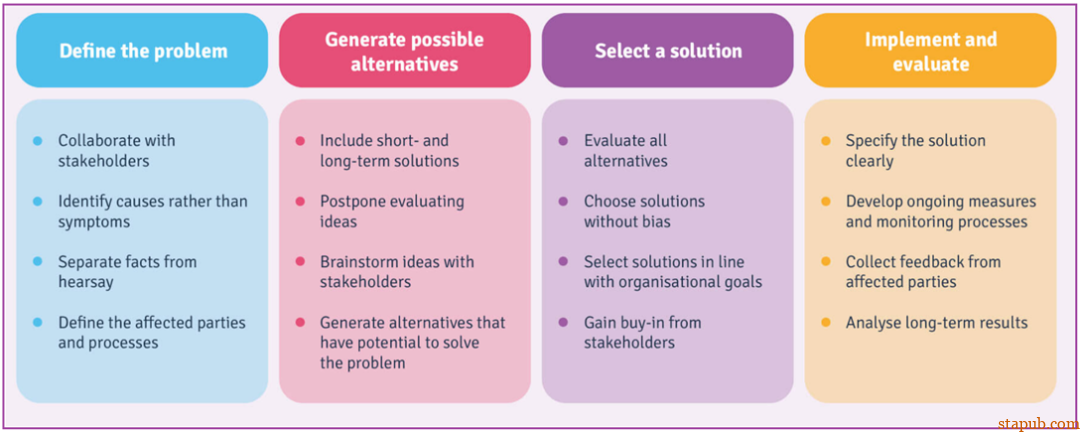
Will this solution fix the problem better than other alternatives? -
Will all your stakeholders agree with using this alternative? -
Does your organisation have the capacity to implement it? -
Is implementation of the solution likely to happen?
-
Transparent communication -
Maintaining open-mindedness -
Refrain from the blame-game -
Connecting the dots.
-
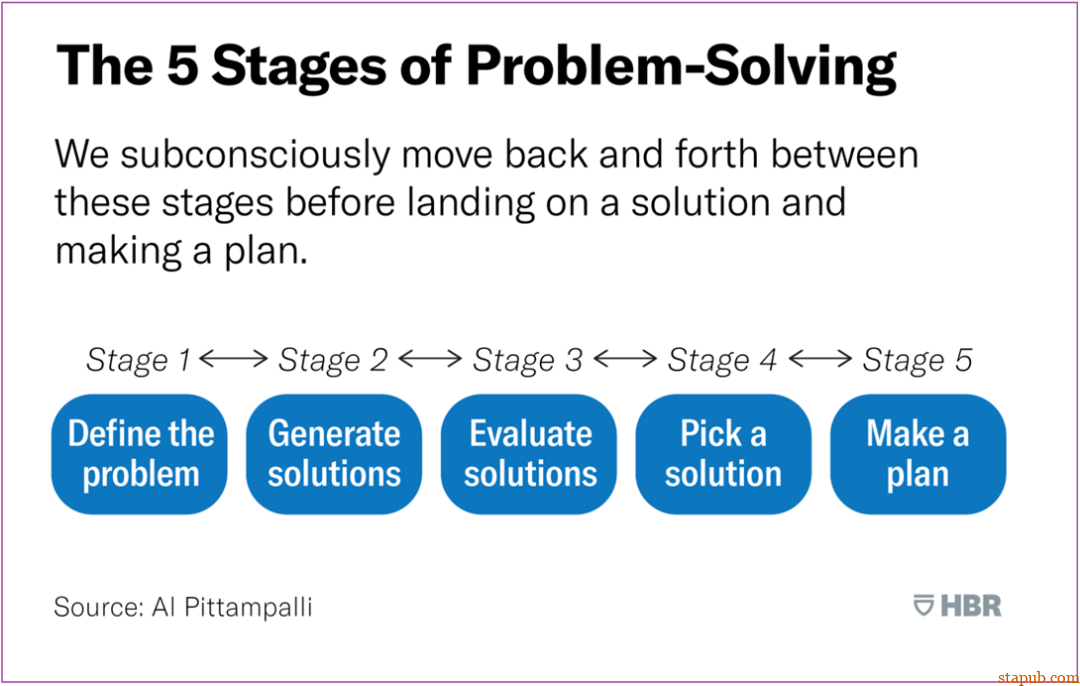
Level 1: The individual doesn’t recognize the problem and doesn’t know how to solve it. -
Level 2: The individual can identify the problem but doesn’t know the solution. -
Level 3: The individual recognizes the problem and has considered multiple solutions, but is unsure which to choose. -
Level 4: The individual identifies the problem, has multiple solutions, and proposes one. -
Level 5: The individual has already encountered a problem, found a solution, and acted on it, and now reports the resolution post-action.
 需要《A 5 Stage Model for Problem Solving》PDF请评论区留言
需要《A 5 Stage Model for Problem Solving》PDF请评论区留言-
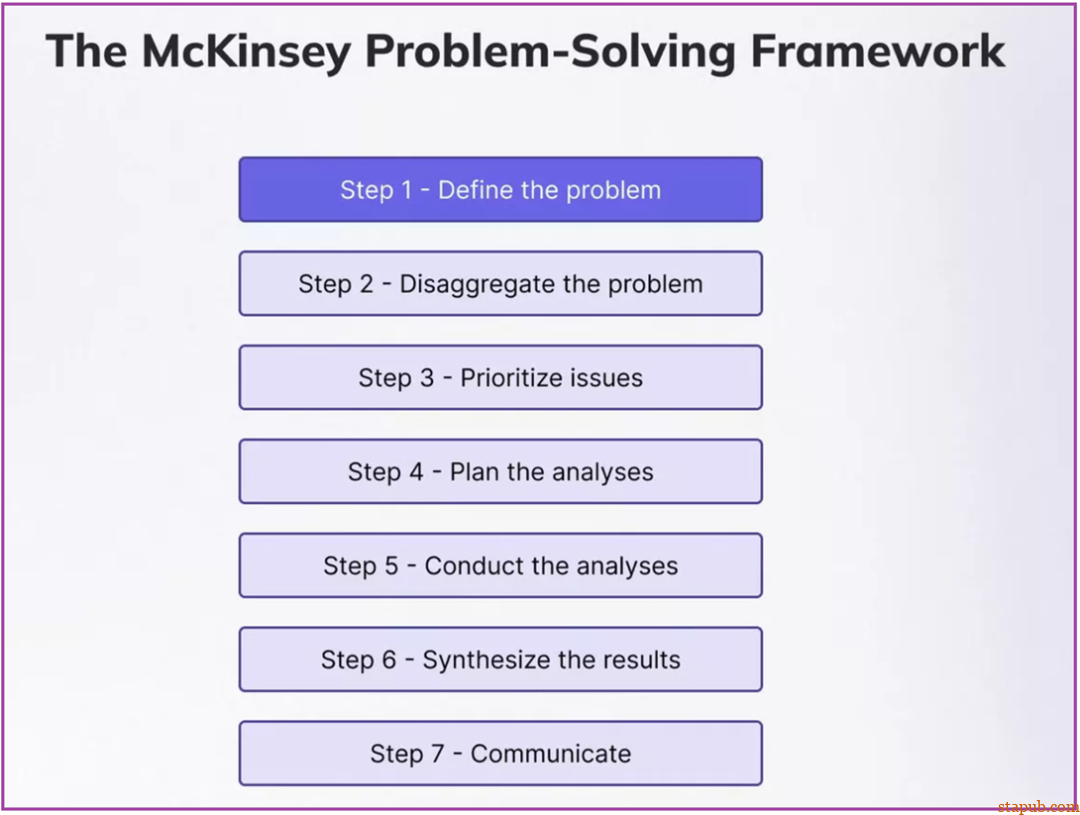
定义问题(Define the problem):与所有利益相关者合作,明确需要解决的挑战。 -
分解问题(Break down the problem):使用假设树和MECE 原则(互斥、集体穷尽Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive)等工具将问题分解为可管理的部分。 -
确定问题优先级(Prioritize issues):通过使用价值与努力等优先级矩阵,重点关注影响力大、易于实施的解决方案。 -
提出假设(Develop hypotheses):形成假设来指导数据分析并确保关注最可能的解决方案。 -
分析数据(Analyze data):使用数据驱动的方法来检验假设、验证假设并发现见解。 -
综合发现(Synthesize findings):使用金字塔原理总结见解——从详细分析支持的关键建议开始。 -
深度沟通(Deep Communicate):向利益相关者提出清晰、简洁的建议和解决方案;确保他们理解背后的原因和数据,以确保他们的认同。
-
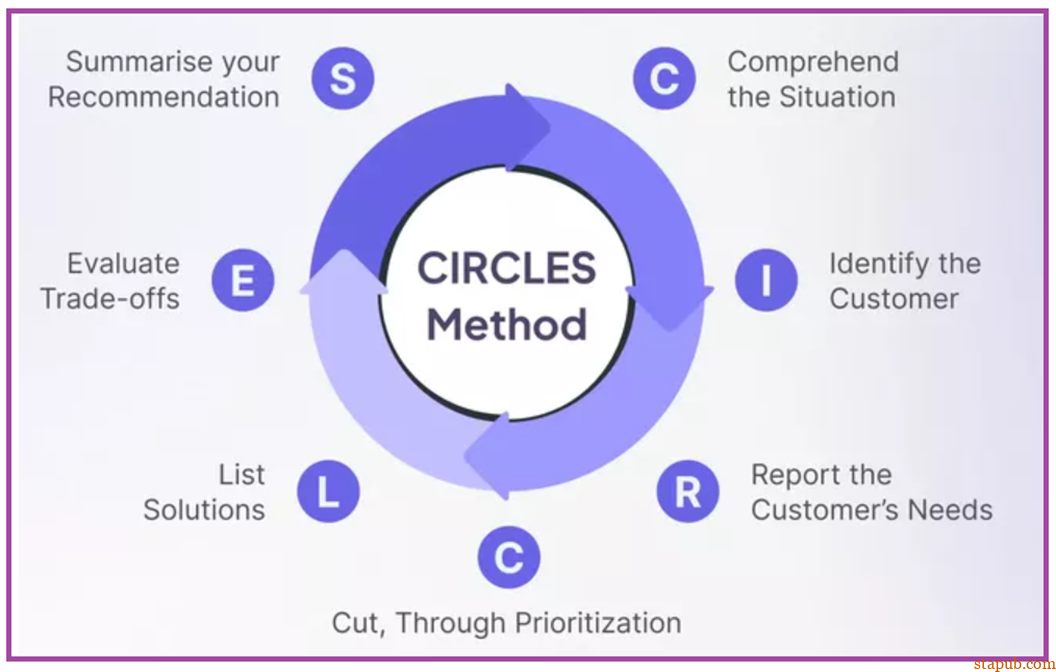
理解情况(C=Comprehend the situation):了解产品团队要解决的问题的背景和细节。 -
识别客户(I=Identify the customer):定义组织产品的目标受众。 -
报告客户需求(R=Report the customer’s needs):进行用户研究,确定客户的痛点和需求。将其记录为用户故事。 -
通过优先排序(C=Cut, through prioritization):使用选择框架来查明最关键的问题。 -
列出解决方案(L=List solutions):集思广益,提出满足客户需求的解决方案。 -
评估权衡(E=Evaluate tradeoffs):权衡可能的解决方案的利弊,考虑其影响、风险和可行性。 -
总结建议(S=Summarize recommendations):选择最佳解决方案并清楚地解释产品团队的决定。
-
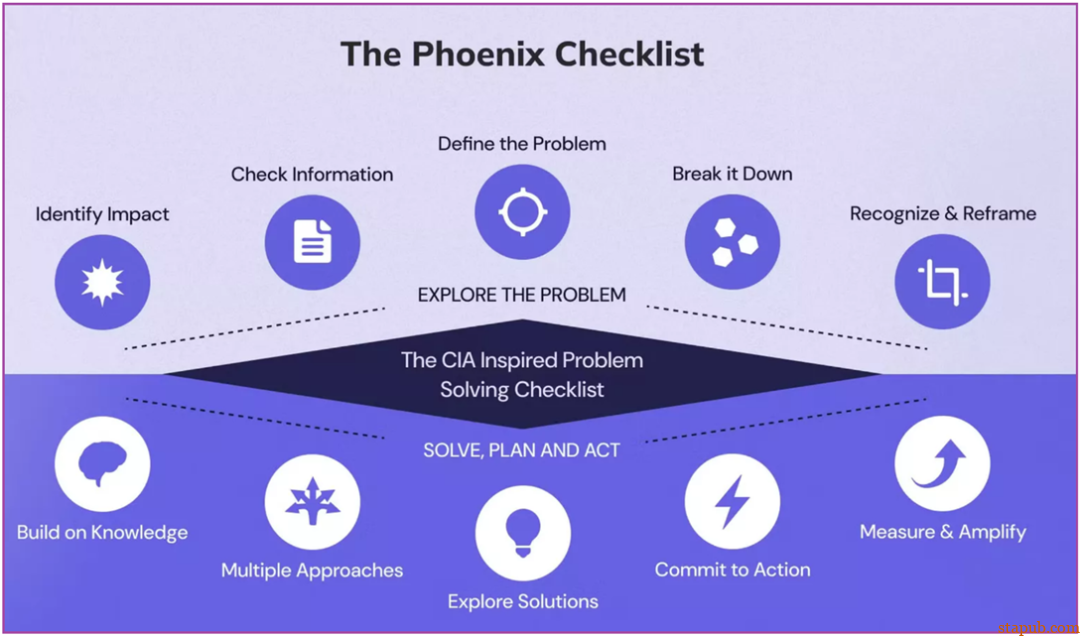
明确需求(Clarify the need):为什么需要解决这个问题?解决这个问题会带来什么好处? -
收集信息(Gather information):有什么信息?这些信息足够吗?未知数有哪些? -
提出问题(Frame the problem):问题的极限是什么?常数是什么? -
分解问题(Break down the problem):能区分问题的不同部分吗?问题的不同部分之间有什么关系?能用图表描述问题吗? -
利用过去的解决方案(Leverage past solutions):以前见过这个问题吗?能用类似问题的解决方案来解决这个问题吗? -
可视化设想解决方案(Visualize solutions):能想象到的最好结果是什么?最坏的结果是什么?最有可能的结果是什么?
-
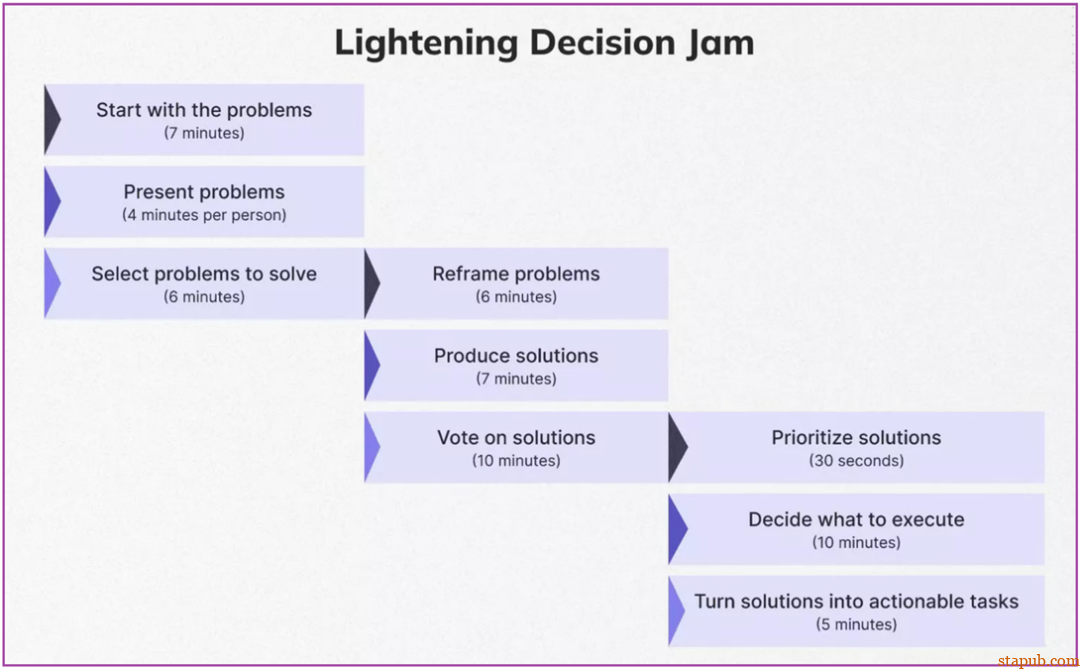
从问题开始(Start with the problems):识别并写下需要解决的问题。 -
提出问题(Present problems):每个参与者提出他们发现的问题。 -
选择要解决的问题(Select problems to solve):使用优先级排序方法来选择需要关注的关键问题。 -
重新定义问题(Reframe problems):将选定的挑战转化为可操作的问题陈述。例如“我们如何简化入职流程以减少用户流失并提高完成率?” -
提出解决方案(Produce solutions):集思广益并为重新构建的问题提出解决方案。 -
对解决方案进行投票(Vote on solutions):使用点投票或类似方法对解决方案进行优先排序。 -
确定解决方案的优先顺序(Prioritize solutions):根据投票确定最佳解决方案。 -
决定执行什么(Decide what to execute):选择立即采取哪些解决方案。 -
将解决方案转化为可操作的任务(Turn solutions into actionable tasks):将选定的解决方案分解为具有责任和期限的明确、可操作的任务。
-
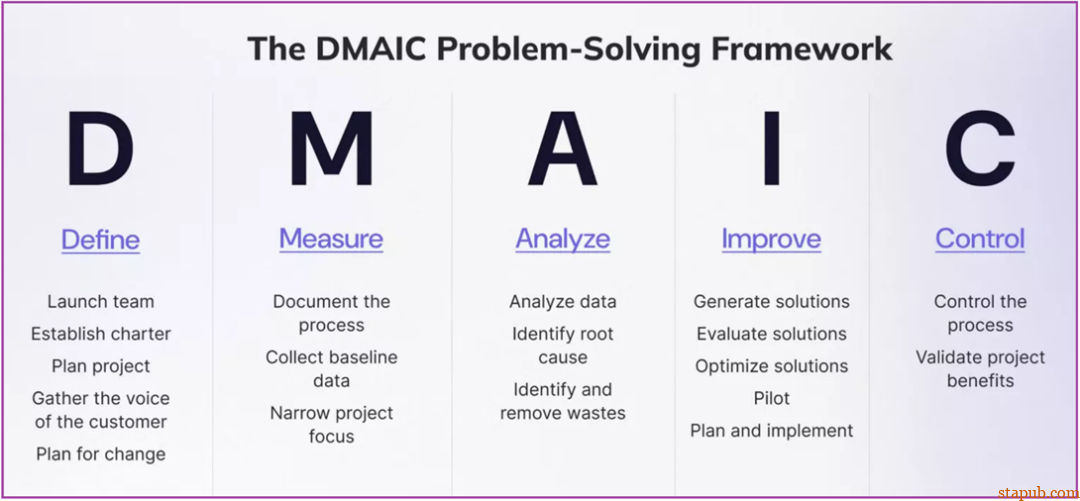
定义阶段(Definition stage):确定问题,汇集必要的人才和资源,并获取客户的声音。确保解决方案符合客户需求。 -
测量阶段(Measure phase):规划流程并测量当前性能以建立改进的基线。 -
分析阶段(Analyze stage):使用数据来识别问题的根本原因并突出显示任何浪费或不增值的活动。 -
改进阶段(Improve stage):生成、测试和优化解决方案。如果测试成功,则制定实施计划。 -
控制阶段(Control phase):确保每个人都遵循新流程并评估结果以确保长期改进。
-
???? ?????????????(???)找出问题的真正根源,以防止将来出现问题。 -
?????? ????????利用创造力开发以用户为中心的解决方案。 -
???? ????????评估优势、劣势、机会和威胁,以制定战略计划。 -
6????????????从多个角度看待问题,做出平衡的决策。 -
????? ?????????????可视化和改进流程以实现最大价值。

-
《Decode and Conquer》By Lewis C. Lin -
《Move Fast and Fix Things: The Trusted Leader’s Guide to Solving Hard Problems.》By Anne Morriss -
Listen to the full HBR IdeaCast episode: How to Solve Tough Problems Better and Faster (2023) -
Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast -
Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org. -
https://userpilot.com/blog/problem-solving-framework/ -
https://acorn.works/enterprise-learning-management/problem-solving
正文完











 hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world