共计 3292 个字符,预计需要花费 9 分钟才能阅读完成。
FPY(First Pass Yield) 与 RTY(Roll ThroughPut Yield)
为什么RTY比FPY更适合?
作为过程质量的衡量标准,效益是6西格玛的重要前提。 有两种类型的效益计算方式:第一次通过率或FPY和滚动产量产量或RTY。 本文比较滚动通过率与第一次通过率。 并解释了如何根据六西格玛方法计算方法。
我们通过如下及部分进行学习:
- yield的含义及定义
- First-pass yield or Throughput yield (FPY)
- 图解– FPY
- Rolled-throughput Yield (RTY)
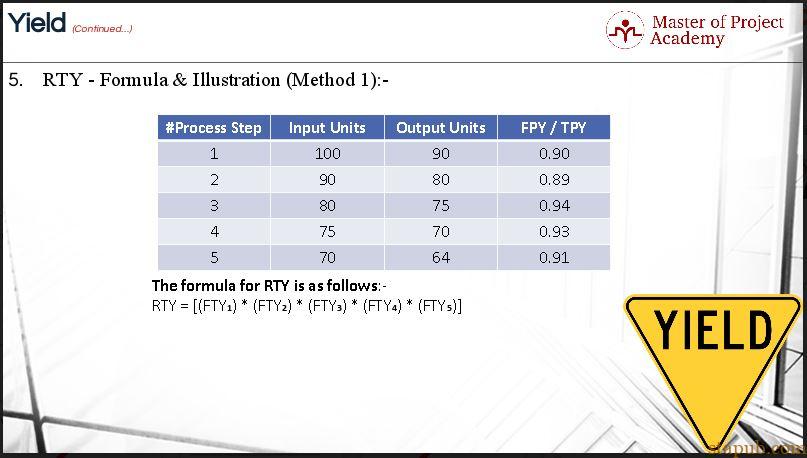
- RTY – 公式及图解 (方法 1)
- RTY – 公式及图解(方法 2)
Yield在精益生产中的定义
收益是精益生产中的一项关键指标。 精益生产中的Yield或FPY或RTY仅仅是产生的良品与总加工数量的比率。 以下是“unit”一词的解释。unit可以是正在进行的任何项目。
两种类型的Yield
First-pass yield (FPY)
有不同的方法来定义收益率,或者您也可以将其称为收益率类型。第一个是第一次通过率,缩写为FPY。它也是已知的第一次产量或产率。这是一个基于单位的指标。第一次产量的缺点是它忽略或不考虑带有一个或多个缺陷的废品的任何返工。在这种情况下,在进行任何“检查”以确定单元是否良好之后进行计算。
让我们看一下第一次产量或吞吐量产量公式的说明。我们正在寻找BPO公司的电子邮件回复流程,该公司作为公用事业和能源公司的服务提供商。我们正在查看电子邮件的数量,即550;这是由一组客户服务人员回应的。在将这些电子邮件发送给客户之前,所有这些电子邮件都经过了检查或质量检查。在质量审核期间,发现203封电子邮件携带大量错误或缺陷。作为纠正练习的一部分,在203封电子邮件中,190个被重新编写并发送回电子邮件处理队列。此外,13封电子邮件的回复非常糟糕,根本无法发送给客户。
因此;该过程的第一次产量或吞吐量产量公式将为347除以550.这给出了0.630或63.09%。我们是怎么到达347的?这是550(电子邮件总数)减去203(缺陷)的结果。当我们想要计算最终发送给客户的电子邮件数量时,我们会从电子邮件总数中减去缺陷数量(13)。
Rolled-throughput Yield (RTY)
现在让我们讨论滚动产量的概念。 首字母缩略词是RTY。 RTY意味着什么? RTY是衡量整体过程质量水平的指标。 它通过将每个过程步骤的DPMO相乘来总结过程或产品的DPMO数据。滚动产量收率是首过率产量的首选收率计算方法。
RTY小于任何单个过程的最低产量。 每个流程步骤始终具有最小和最大产量。 随着处理步骤数量的增加,RTY指数变小。
现在让我们看一下RTY的例子。 我们将讨论两个计算RTY的公式。 我们来看看第一个。
Illustrations of RTY
First method to calculate RTY
We’ve got 5 process steps in this example. Each step has got input units and output units. Input units are the ones entering each process step, and output units refer to good units produced by each process step. With the help of a formula, we’ve got the first pass yield for each process step. To calculate RTY, multiply the FPY of each process steps to get the answer. In this case, your equation will be the multiplication of five FPY values which will result in 0.6372. In other words, your RTY for all process steps is 63.72%. That was the first throughput yield formula.
Second method to calculate RTY
Let us have a look at the second method of RTY calculation. We’ve again got 5 process steps in this example. To use this method; you need to have two metrics i.e. DPMO and DPU calculated for each process step.
We will now review the calculations to determine the DPU and DPMO.
Calculation of DPU
- Determine the number of units
- Count the number of defects
- Divide the number of defects by the number of units
Calculation of DPMO
- Determine the number of units
- Determine the number of defect opportunities per unit
- Determine the total number of defect opportunities for all the units by multiplying the number of defects per opportunity by the total number of units
- Count the units with defects in the total sample by counting how many opportunities within the sample group contained defects or errors
- Divide the total defects by the total opportunities and multiply by a million
Another simple way to calculate DPU
In this example, we’ve calculated DPU using another quick formula. We’ve divided DPMO figure by 1 million to get DPU for each process step. Why did we do that? DPMO incorporates 1 million defect opportunities, and we need to know defect opportunities for each unit. That is why we divided DPMO by 1 million.
Calculating the RTY from the DPU
In the next column, we have deducted DPU from 1 to get the first-pass yield (FTY) for each process step. The 1 refers to 100%. The logic here is simple. The 100% yield for each process step minus defect opportunities per-unit for each process step is equivalent to good units produced by each process step. In this method, the RTY is calculated by multiplying the FTY for each process as determined in the previous step to get the RTY.
RTY is a realistic view of the yield of any process, looking at all the process steps. The RTY of a process is a good measure of the quality of a process. If the RTY is too low, then a problem-solving team needs to investigate how the process can be improved.








 透彻理解卡方检验 - 汽车质量管理笔记
[…] 化简后的式子是我们在卡方检验中需要用到的式子,所以请大家牢记!对于上述式子有疑惑的读者可以学习基础的概率论,也可以参考我之前写的一篇关于独立的文章(《【直观数学】如何理解两事件间的独立关系》)。如果没有问题的话,我们可以进入到卡方检验原理与步骤的主体介绍部分! […]
透彻理解卡方检验 - 汽车质量管理笔记
[…] 化简后的式子是我们在卡方检验中需要用到的式子,所以请大家牢记!对于上述式子有疑惑的读者可以学习基础的概率论,也可以参考我之前写的一篇关于独立的文章(《【直观数学】如何理解两事件间的独立关系》)。如果没有问题的话,我们可以进入到卡方检验原理与步骤的主体介绍部分! […]